Quality Tungsten Carbide Ball
Basic Info
Model No.: P05, P10, P20, P30, P35, P40, M10, M20, M30, M40, K01, K05, K10, K15
Product Description
Quality Tungsten Carbide Ball
Description:
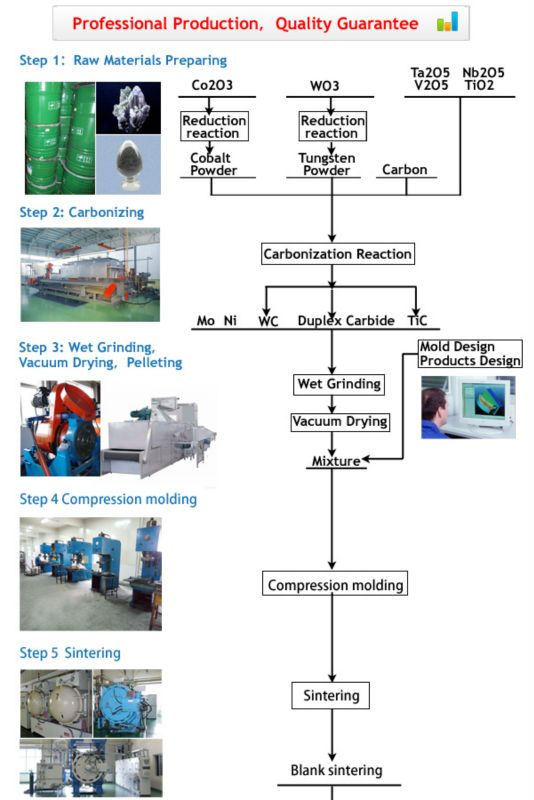
Tungsten carbide ball are widely used in ball valve and bearing. We can offer
various grades and sizes. And the requirements of each procedure are stringent
to ensure that the products produced must comply with your request. We adopt
the advanced technical. The ball has the high endured causticity and high endure
grind, which could improve the life of the bearing, while elevate the value of
your products.
Sintered ball:
| Specifications: | ISO K10 and K20 are most common | ||||||
| Material Composition | Typical Material composition is | ||||||
| 6% Cobalt | |||||||
| 94% Tungsten Carbide | |||||||
| But other compositions are available with Cobalt content up to 25%. Hardness reduces and toughness increases with increasing cobalt content. | |||||||
| Hardness | 1500 to 1600 HV | ||||||
| Corrosion Resistance | Cobalt binder material is reasonably resistant to corrosion. The Cobalt binder will corrode in contact with water, but the effect is largely cosmetic in that the balls loose their polished appearance, with little effect on performance. De-ionised water does pose a more severe problem, as it can tend to promote 'leeching' of Cobalt from the binder. Erosion of the binder can be a problem when in contact with abrasive particles as may occur in some valve and pump applications. | ||||||
| Special Properties | Hardness if retained to approx. 800 degrees Celsius. Balls can be brazes to steel stems to allow mounting, or hole may be produced by spark erosion. | ||||||
| Availability | Balls are made in a wide range of sizes from 0.4mm to 100mm and can be made in larger sizes. | ||||||
| Applications | Valves, Pumps, Ball Screws, Measurement Standards, Gauging, Wear Parts. | ||||||
| General Information | Cobalt Binder Tungsten Carbide is in many ways an ideal material for ball production. Its hardness and stiffness allows the production of extremely accurate balls, with very fine control of final size. The material is extremely stable and these properties make Tungsten Carbide Balls and ideal choice for reference standards in metrology. Equally, the same properties make the balls and ideal choice for all applications where wear rates need to be low. | ||||||
Finished ball:
| Tungsten carbide ball are widely used in ball valve and bearing. We can offer various grades and sizes. And the requirements of each procedure are stringent to ensure that the products produced must comply with your request. We adopt the advanced technical. The ball has the high endured causticity and high endure grind, which could improve the life of the bearing, while elevate the value of your products. | |||||||
| Material Composition | |||||||
| Typical Material composition: 6% Cobalt, 94% Tungsten Carbide. | |||||||
| But other compositions are available with Cobalt content up to 25%. Hardness reduces and toughness increases with increasing cobalt content. | |||||||
| Corrosion Resistance | |||||||
| Cobalt binder material is reasonably resistant to corrosion. The Cobalt binder will corrode in contact with water, but the effect is largely cosmetic in that the balls loose their polished appearance, with little effect on performance. De-ionised water does pose a more severe problem, as it can tend to promote 'leeching' of Cobalt from the binder. Erosion of the binder can be a problem when in contact with abrasive particles as may occur in some valve and pump applications. |
Note: Tungsten carbide ball of various diameter and size combinations can be supplied
at customer's request.
Display:







Q:What is cemented carbide ?
A:Cemented carbide is a hard material used in machining tough materials such as carbon steel or
stainless, as well as in situations where other tools would wear away, such as high-quantity
production runs. Most of the time, carbide will leave a better finish on the part, and allow faster
machining. Carbide Tools can also withstand higher temperatures than standard high speed steel tools.
Q:What is the difference between cemented and tungsten carbide?
A:Cemented carbides consist of hard grains of the carbides of transition metals (Ti, V, Cr, Zr, Mo,
Nb, Hf, Ta, and/or W) cemented or bound together by a softer metallic binder consisting of Co,
Ni, and/or Fe (or alloys of these metals). Tungsten carbide (WC), on the other hand, is a compound
of W and C. Since most of the commercially important cemented carbides are based on WC as
the hard phase, the terms "cemented carbide" and "tungsten carbide" are often used interchangeably.
Q:What are the key properties of cemented carbides I should be concerned with when
selecting a grade for my application?
A: The key properties of cemented carbides that define their performance level for different
applications include abrasion resistance (directly related to the hardness of the grade),
fracture strength, and fracture toughness. In general, the abrasion resistance or hardness of any grade
is inversely proportional to its fracture toughness. Very often grade selection involves finding the best
compromise between abrasion resistance and toughness. In some instances strength and corrosion
resistance can be important factors in the grade selection process.
Q: Which grade characteristics affect the properties of cemented carbide?
A: The properties of cemented carbides are affected by four primary material characteristics,
namely,( 54490904,i) the average grain size of the carbide phase,( 54490905,ii) the weight or volume percent of the
binder alloy present,( 54490906,iii) the composition of the carbide phases, and (iv) the composition of the
binder alloy. In general, hardness increases (and fracture toughness decreases) as the average hard
phase grain size decreases and/or the weight or volume fraction of the binder decreases.
The strength increases as the average grain size of hard phase decreases at any given binder fraction.
Corrosion resistance increases as Ni and/or Cr is substituted for Co in the binder alloy.
Q: Which properties are important in metal cutting applications?
A: Depending upon the type of metalcutting operation (turning, Milling, drilling, etc.), different
combinations of properties is needed in order to obtain optimum results. For example, in turning
and drilling applications the cutting tool is in continuous contact with the workpiece. Hence,
for these applications, abrasion resistance and strength are the most important properties to consider.
However, in operations such as milling, which invariably involve interrupted cutting, and hence high
impact forces, toughness can be an important factor. Grades employed for metalcutting applications
are usually based on fine to medium hard phase grain sizes (0.5 to 1.5 mm) and low to medium
Co contents (6 to 15 wt.%).

Product Categories : Tungsten Carbide > Tungsten Ball
Premium Related Products














